Views: 222 Author: Lake Publish Time: 2025-11-16 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Understanding Shelf Life and Expiration Dates
● Single-Use Duration and Wear Time
● Material Degradation and Performance Maintenance
● Storage Conditions and Environmental Factors
● Reusable Isolation Gowns: Lifespan and Reprocessing
● Regulatory Standards and Compliance
● Economic Considerations and Inventory Management
● Emergency Preparedness and Strategic Stockpiling
>> 1. What is the typical shelf life of disposable isolation gowns?
>> 2. Can isolation gowns be used after their expiration date?
>> 3. How long can a single isolation gown be worn during patient care?
>> 4. What factors affect the longevity of reusable isolation gowns?
>> 5. How should isolation gowns be stored to maximize their shelf life?
The question of how long isolation gowns remain effective and safe for use encompasses multiple dimensions of healthcare product management, infection control, and regulatory compliance. Understanding the functional lifespan of isolation gowns requires examining manufacturer specifications, material durability, storage conditions, and usage patterns. The longevity of isolation gowns varies significantly between disposable and reusable variants, with each type presenting distinct considerations for shelf life, wear duration, and performance maintenance. This comprehensive analysis explores the factors determining the effective service life of isolation gowns, providing healthcare facilities, procurement specialists, and infection control professionals with essential knowledge for optimizing the use and management of these critical protective garments.

Isolation gowns, particularly disposable versions, typically come with manufacturer-specified expiration dates that indicate the period during which the product maintains its intended performance characteristics. The shelf life of isolation gowns is determined through rigorous stability testing that assesses material degradation, barrier integrity, and fastener functionality over time. Most disposable isolation gowns have a shelf life ranging from three to five years when stored under appropriate conditions. These expiration dates for isolation gowns ensure that the protective barriers remain effective against fluid penetration and microbial transmission.
The determination of shelf life for isolation gowns involves accelerated aging studies that simulate long-term storage conditions. Manufacturers of isolation gowns conduct these tests according to standardized protocols, establishing expiration dates based on demonstrated maintenance of performance standards. Healthcare facilities must implement inventory management systems that prioritize the use of isolation gowns based on their manufacturing dates, ensuring that older stock is utilized first. Proper rotation of isolation gowns inventory prevents the use of expired products that may have compromised protective qualities, maintaining the safety standards essential in healthcare environments.
The functional wear time of isolation gowns during clinical use represents a critical aspect of their effective lifespan. Disposable isolation gowns are designed for single use during a single patient encounter or specific procedure. The maximum wear time for isolation gowns depends on the procedure type, exposure risk, and manufacturer recommendations. Generally, isolation gowns should be removed and discarded immediately after completing the task for which they were donned, or whenever they become contaminated. Extended wear of the same isolation gowns across multiple patient interactions significantly increases cross-contamination risks.
Healthcare protocols typically dictate that isolation gowns should be changed between patients, after contact with potentially infectious materials, and when moving from contaminated to clean areas. The durability of isolation gowns during wear depends on their material composition and construction quality. While some heavy-duty isolation gowns may physically withstand multiple uses, their protective barriers can become compromised through microscopic tears or fluid penetration that may not be visibly apparent. Adhering to single-use protocols for disposable isolation gowns ensures consistent protection for both healthcare workers and patients.
The materials used in isolation gowns undergo natural degradation processes that affect their protective capabilities over time. Nonwoven fabrics common in disposable isolation gowns can experience fiber breakdown, reduced tensile strength, and diminished liquid barrier performance as they age. Environmental factors including temperature fluctuations, humidity exposure, and ultraviolet light can accelerate the degradation of isolation gowns materials. Manufacturers conduct extensive testing to establish expiration dates that account for these material changes, ensuring isolation gowns maintain their protective integrity throughout their shelf life.
The elastic components, ties, and fasteners on isolation gowns represent additional elements subject to performance degradation. These critical components of isolation gowns can lose elasticity or strength over time, compromising the secure fit necessary for effective protection. The barrier coatings applied to isolation gowns for fluid resistance may also deteriorate, reducing their effectiveness against liquid penetration. Regular assessment of isolation gowns inventory for signs of material degradation, such as discoloration, stiffness, or visible damage, helps healthcare facilities identify products that may no longer provide adequate protection despite being within their stated expiration period.
Proper storage conditions significantly influence the functional longevity of isolation gowns. Manufacturers provide specific storage recommendations for isolation gowns that typically include maintaining cool, dry environments away from direct sunlight and chemical exposure. Ideal storage conditions for isolation gowns involve temperature control between 15-30°C (59-86°F) and relative humidity below 80%. Exposure to extreme temperatures or humidity can accelerate the degradation of isolation gowns materials, potentially reducing their effective shelf life below the manufacturer's stated expiration date.
Healthcare facilities must implement appropriate storage protocols for isolation gowns to preserve their protective qualities. Isolation gowns should be stored in their original packaging until ready for use, protecting them from environmental contaminants and physical damage. Proper stacking and handling of isolation gowns packages prevent compression damage that could affect material integrity. Inventory management systems for isolation gowns should include regular inspections of storage areas to ensure environmental conditions remain within recommended parameters, preserving the performance characteristics of these essential protective garments throughout their intended shelf life.
Reusable isolation gowns present different considerations regarding functional lifespan compared to their disposable counterparts. The service life of reusable isolation gowns is typically measured in number of laundering cycles rather than time-based expiration. High-quality reusable isolation gowns can withstand 50 to 100 laundering cycles while maintaining their protective properties, though this varies based on material composition, construction quality, and reprocessing methods. Healthcare facilities utilizing reusable isolation gowns must implement tracking systems to monitor usage cycles and remove garments that have exceeded their recommended lifespan.
The reprocessing procedures for reusable isolation gowns significantly impact their longevity and maintained protection levels. Industrial laundering of isolation gowns involves specific protocols for washing, drying, and inspection that preserve material integrity and barrier properties. Proper reprocessing of isolation gowns includes visual inspections for damage, integrity testing, and repairs when appropriate. The gradual degradation of reusable isolation gowns through multiple laundering cycles necessitates established criteria for retirement, ensuring that only fully protective garments remain in clinical circulation.
The shelf life and usage specifications for isolation gowns fall under regulatory oversight to ensure consistent protection standards. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates isolation gowns as medical devices, requiring manufacturers to establish and validate expiration dates through appropriate stability testing. These regulations for isolation gowns ensure that healthcare providers receive products with reliably maintained performance characteristics throughout their stated shelf life. Compliance with these standards requires manufacturers of isolation gowns to conduct real-time and accelerated aging studies that demonstrate maintained barrier protection and material integrity.
Healthcare facilities utilizing isolation gowns must adhere to regulatory requirements regarding product expiration and usage. The Joint Commission and other accreditation bodies include standards for medical device management that encompass the proper storage, rotation, and use of isolation gowns. Documentation practices for isolation gowns inventory should include manufacturing dates, expiration dates, and lot numbers to facilitate tracking and recall capabilities. Regular audits of isolation gowns management practices help healthcare organizations maintain compliance with regulatory standards while ensuring the consistent availability of effective protective equipment for clinical staff.
The effective management of isolation gowns inventory requires balancing product availability with shelf life considerations. Healthcare facilities must implement inventory rotation systems that ensure older isolation gowns are used before newer stock, minimizing waste from expired products. The economic impact of expired isolation gowns can be significant, particularly for facilities maintaining large inventories for emergency preparedness. Strategic purchasing of isolation gowns based on usage patterns and storage capacities helps optimize inventory levels while preserving product effectiveness.
The cost-benefit analysis between disposable and reusable isolation gowns involves considerations beyond initial acquisition costs. While reusable isolation gowns typically have higher upfront costs, their extended lifespan through multiple use cycles may offer long-term economic advantages. However, the reprocessing expenses for reusable isolation gowns, including laundering, inspection, and repair, must be factored into total cost calculations. Healthcare facilities must also consider the storage space requirements for maintaining adequate inventories of isolation gowns, whether disposable or reusable, to meet clinical needs without compromising product quality through improper storage conditions.
The shelf life of isolation gowns takes on particular importance in the context of emergency preparedness and strategic stockpiling. Healthcare facilities and public health organizations maintain inventories of isolation gowns for pandemic response and emergency situations. The management of these stockpiled isolation gowns requires careful attention to expiration dates and rotation schedules to ensure product viability when needed. Extended shelf life testing for isolation gowns intended for strategic stockpiles may provide data supporting use beyond typical expiration periods during declared emergencies.
The monitoring and maintenance of stockpiled isolation gowns involves regular inspection, environmental monitoring, and inventory rotation. Some regulatory agencies provide guidance on the extended use of expired isolation gowns during declared emergencies when replacement supplies are unavailable. However, such use of isolation gowns beyond their manufacturer-stated expiration requires risk assessment and appropriate disclosure to healthcare workers. The development of robust supply chains for isolation gowns helps reduce the need for extended stockpiling, ensuring healthcare facilities can access fresh products while maintaining emergency preparedness.
The functional lifespan of isolation gowns encompasses multiple dimensions including shelf life, single-use duration, and for reusable variants, laundering cycle longevity. Disposable isolation gowns typically maintain their protective qualities for three to five years when stored under appropriate conditions, while reusable isolation gowns may withstand 50-100 laundering cycles before requiring replacement. The effective service life of isolation gowns depends on proper storage, handling, and adherence to usage protocols that preserve their barrier integrity and protective capabilities.
Healthcare facilities must implement comprehensive management systems for isolation gowns that address inventory rotation, storage conditions, and usage protocols. Understanding the factors that influence the longevity of isolation gowns enables healthcare organizations to optimize their protective equipment resources while maintaining infection control standards. As material technologies advance, the development of isolation gowns with extended shelf lives and enhanced durability may offer improvements in both protection and resource utilization. The ongoing evaluation of isolation gowns performance throughout their lifespan remains essential for ensuring consistent protection in healthcare environments.
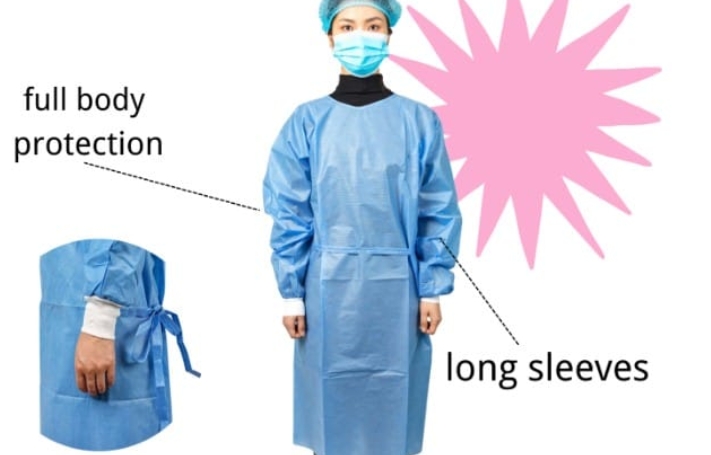
Most disposable isolation gowns have a manufacturer-stated shelf life of three to five years when stored according to recommended conditions. The shelf life of isolation gowns is determined through stability testing that assesses material integrity and barrier performance over time. Healthcare facilities should implement inventory management systems that ensure isolation gowns are used before their expiration dates, as protective qualities may diminish beyond this period.
Using isolation gowns after their expiration date is generally not recommended as the protective barriers may have degraded. The material integrity of expired isolation gowns cannot be guaranteed, potentially compromising protection against fluids and microorganisms. During supply shortages or declared emergencies, regulatory agencies may provide specific guidance regarding extended use of expired isolation gowns, but such use requires risk assessment and appropriate staff notification.
Disposable isolation gowns are designed for single use during a specific procedure or patient interaction. Isolation gowns should be removed and discarded immediately after completing the task for which they were donned, or whenever they become contaminated. Wearing the same isolation gowns for multiple patients or extended periods increases cross-contamination risks and compromises infection control protocols.
The functional lifespan of reusable isolation gowns depends on material quality, construction methods, and reprocessing protocols. Most reusable isolation gowns can withstand 50-100 laundering cycles while maintaining protective properties. The longevity of reusable isolation gowns is affected by washing temperatures, chemical exposures, mechanical stress during laundering, and inspection protocols that identify damage requiring repair or retirement.
Isolation gowns should be stored in their original packaging in cool, dry environments with temperatures between 15-30°C (59-86°F) and relative humidity below 80%. Storage areas for isolation gowns should be protected from direct sunlight, extreme temperatures, and chemical exposure. Proper stacking of isolation gowns packages prevents compression damage, and inventory rotation systems ensure older stock is used first, maximizing product effectiveness throughout its shelf life.
[1] https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/personal-protective-equipment-infection-control/isolation-gowns
[2] https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/isolation/index.html